The power supply configurations for gantry cranes encompass five primary types: cable reel power supply, conductor rail power supply, overhead power supply, trailing cable power supply, and diesel generator power supply.
Conductor rail power supply includes trench-mounted safety conductor rail power supply and low-mounted safety conductor rail power supply. When utilizing 10KV high-voltage power sources, a cable reel power supply or overhead power supply is typically selected.
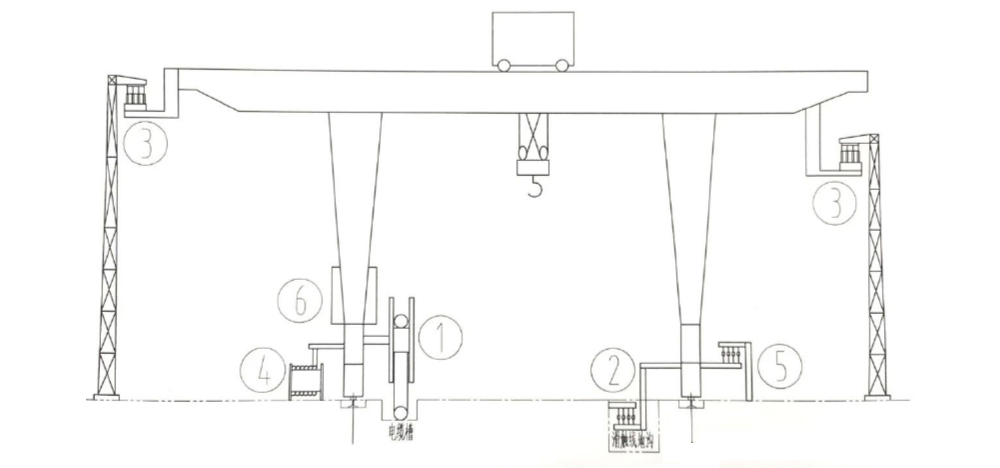 ① Cable reel power supply ② Trench-mounted safety conductor rail power supply ③ Overhead power supply ④ Trailing cable power supply ⑤ Low-mounted safety conductor rail power supply ⑥ Diesel generator power supply
1. Cable Reel Power Supply Principle: During gantry crane operation, the cable reel automatically retracts and extends the cable to supply power.
Advantages: Lower cost, simple installation, and maintenance.
Applicable scenarios: Small to medium-sized gantry cranes and applications with limited working ranges, such as fixed-track gantry cranes in small factories. Typically employs an intermediate power supply. Container gantry cranes often utilize hysteresis cable reels with an intermediate power supply within a ±200m travel range. Travel exceeding 200m requires verification with the equipment manufacturer.
① Cable reel power supply ② Trench-mounted safety conductor rail power supply ③ Overhead power supply ④ Trailing cable power supply ⑤ Low-mounted safety conductor rail power supply ⑥ Diesel generator power supply
1. Cable Reel Power Supply Principle: During gantry crane operation, the cable reel automatically retracts and extends the cable to supply power.
Advantages: Lower cost, simple installation, and maintenance.
Applicable scenarios: Small to medium-sized gantry cranes and applications with limited working ranges, such as fixed-track gantry cranes in small factories. Typically employs an intermediate power supply. Container gantry cranes often utilize hysteresis cable reels with an intermediate power supply within a ±200m travel range. Travel exceeding 200m requires verification with the equipment manufacturer.
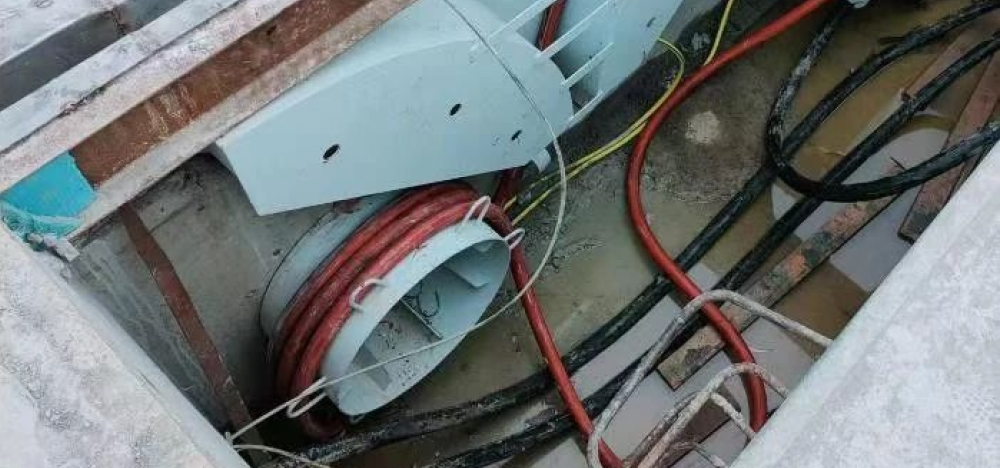

2. Trench-mounted Safety Conductor Rail Power Supply Principle: The gantry crane’s collector contacts the conductor rail installed in a trench alongside the track to obtain electrical power. Advantages: Excellent power supply stability, capable of handling high currents and voltages, suitable for high-power gantry cranes. Provides good resistance to rain, dust, and corrosion. Reduces cable wear and dragging. Multiple gantry cranes can be installed within the same span of time.
Suitable scenarios: Large ports and other locations with high cargo handling volumes and stringent power supply reliability requirements.
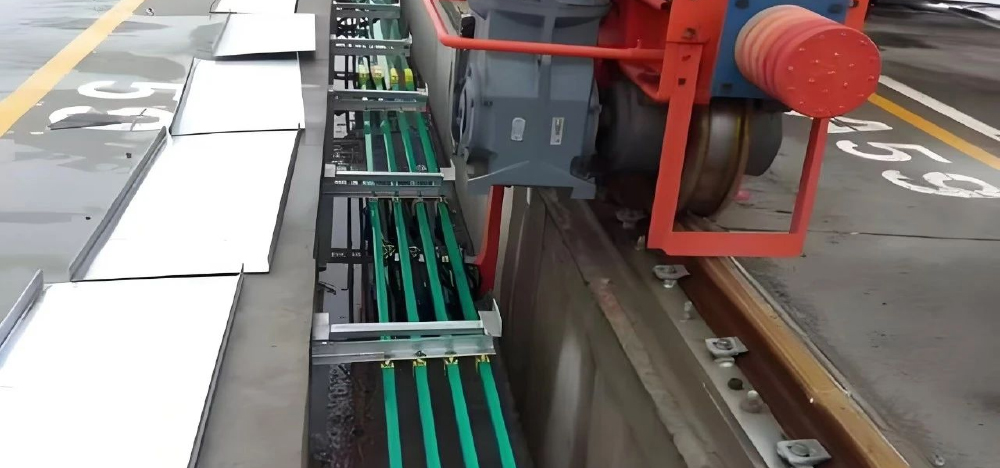 3. Elevated Power Supply Principle: Power cables are installed on concrete poles or steel towers to supply power to gantry cranes. Advantages: Suitable for long operating distances, extended project durations, and areas requiring ground vehicle access. Does not occupy ground space and does not interfere with ground traffic. Suitable Scenarios: Large cargo yards, docks, and similar locations—such as gantry cranes in major ports—where long travel distances require uninterrupted ground traffic flow.
3. Elevated Power Supply Principle: Power cables are installed on concrete poles or steel towers to supply power to gantry cranes. Advantages: Suitable for long operating distances, extended project durations, and areas requiring ground vehicle access. Does not occupy ground space and does not interfere with ground traffic. Suitable Scenarios: Large cargo yards, docks, and similar locations—such as gantry cranes in major ports—where long travel distances require uninterrupted ground traffic flow.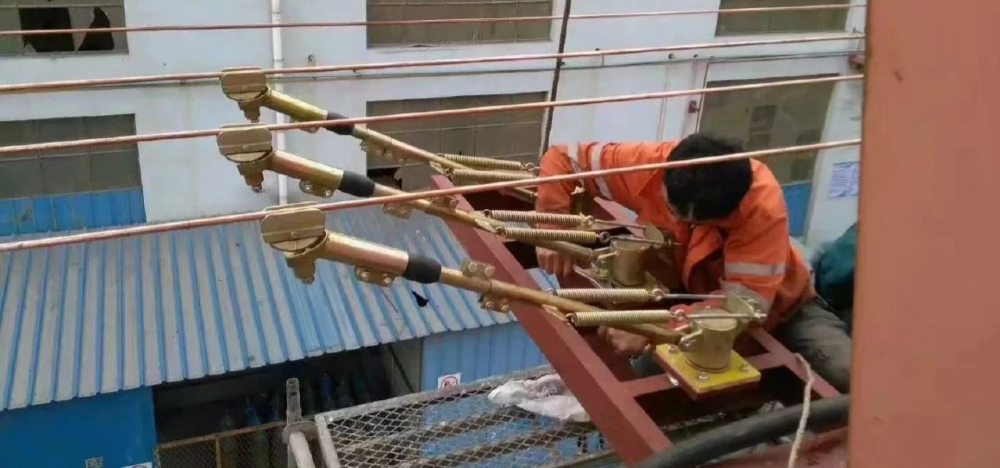
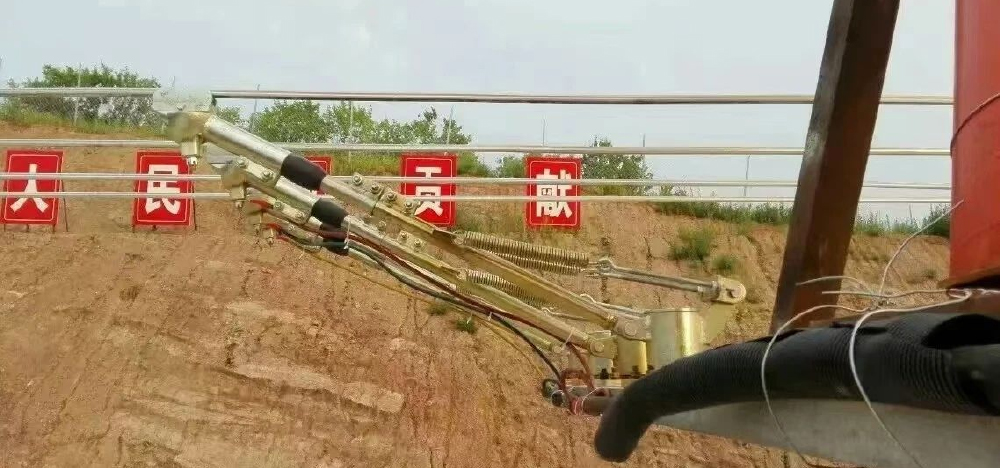 4. Cable-Towing Power Supply Principle: Utilizes flexible cables connected to a power source at one end and the gantry crane at the other, with the cable being towed as the crane moves.
Disadvantages: Cables are prone to wear and require frequent inspection and replacement.
Suitable Scenarios: Gantry cranes with low power requirements and slow operating speeds.
5. Low-Profile Safety Conductor Rail Power Supply Principle: Similar to trench conductor rail power supply, but installed above ground at a low elevation.
Features: High safety, reduces electric shock risk.
Suitable Scenarios: Ideal for retrofitting gantry crane power systems or when crane track foundations were not initially designed for power supply. Also applicable for newly designed gantry cranes.
6. Diesel Generator Power Supply Principle: Diesel generators produce electricity for the gantry crane. The generator room is typically mounted directly beneath the crane’s crossbeam, enabling remote start/stop control with fuel and oil monitoring programs and alarm functions.
Advantages: Independent of external power sources, suitable for remote areas without mains electricity or temporary work sites.
Applicable Scenarios: Off-grid construction sites and other locations without access to mains power.
4. Cable-Towing Power Supply Principle: Utilizes flexible cables connected to a power source at one end and the gantry crane at the other, with the cable being towed as the crane moves.
Disadvantages: Cables are prone to wear and require frequent inspection and replacement.
Suitable Scenarios: Gantry cranes with low power requirements and slow operating speeds.
5. Low-Profile Safety Conductor Rail Power Supply Principle: Similar to trench conductor rail power supply, but installed above ground at a low elevation.
Features: High safety, reduces electric shock risk.
Suitable Scenarios: Ideal for retrofitting gantry crane power systems or when crane track foundations were not initially designed for power supply. Also applicable for newly designed gantry cranes.
6. Diesel Generator Power Supply Principle: Diesel generators produce electricity for the gantry crane. The generator room is typically mounted directly beneath the crane’s crossbeam, enabling remote start/stop control with fuel and oil monitoring programs and alarm functions.
Advantages: Independent of external power sources, suitable for remote areas without mains electricity or temporary work sites.
Applicable Scenarios: Off-grid construction sites and other locations without access to mains power.
Post Views: 5





